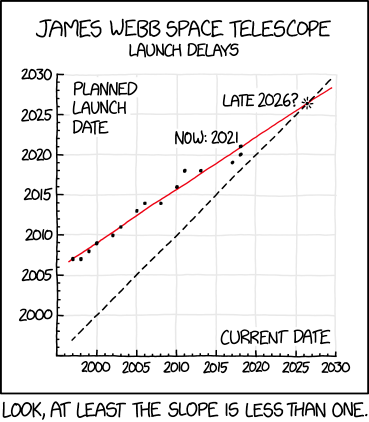
I was talking (well, via video) to a friend about the James Webb Telescope. The James Webb is going to be a pretty big deal when it launches. It is one of the most complex things designed by humans, and it will do a lot more than the Hubble telescope, which means we can learn more about space, and, well, who knows?
When is it due to launch? It’s been delayed quite a few times. There’s even a relevant XKCD on this:
And, looking at this, I was wondering how accurate the plot Randall Munroe made was? Turns out this was an interesting exercise in itself!
This blog post covers how to scrape some tables from Wikipedia, tidy them up, perform some basic modelling, make some forecasts, and plot them.
The packages
First let’s load up a few libraries:
library(polite)
library(rvest)
#> Loading required package: xml2
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching packages ───────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.0 ──
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.3.2 ✔ purrr 0.3.4
#> ✔ tibble 3.0.4 ✔ dplyr 1.0.2
#> ✔ tidyr 1.1.2 ✔ stringr 1.4.0
#> ✔ readr 1.4.0 ✔ forcats 0.5.0
#> ── Conflicts ──────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ readr::guess_encoding() masks rvest::guess_encoding()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
#> ✖ purrr::pluck() masks rvest::pluck()
library(janitor)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'janitor'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> chisq.test, fisher.test
conflicted::conflict_prefer("pluck", "purrr")
#> [conflicted] Will prefer purrr::pluck over any other package
politeandrvestare the webscraping toolstidyversegives us many data analysis toolsjanitorprovides some extra data cleaning powers.
We also use conflicted to state we prefer pluck from the purrr package (as there is a pluck in rvest, which has caught me out many a time).
First, let’s take a look at the Wiki article to get the data and the dates.
It looks like this table is what we want:
But how do we download the table into R?
We “inspect element” to identify the table (CMD + Shift + C on Chrome):
Mousing over the table we see that this has the class: “wikitable”. We can use this information to help extract out the right part of the website.
First, let’s use the polite package to check we can download the data:
wiki_url <- "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Webb_Space_Telescope"
bow(wiki_url)
#> <polite session> https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Webb_Space_Telescope
#> User-agent: polite R package - https://github.com/dmi3kno/polite
#> robots.txt: 456 rules are defined for 33 bots
#> Crawl delay: 5 sec
#> The path is scrapable for this user-agent
Ok looks like we are all good! Now let’s scrape it.
jwebb_data <- bow(wiki_url) %>% scrape()
jwebb_data
#> {html_document}
#> <html class="client-nojs" lang="en" dir="ltr">
#> [1] <head>\n<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8 ...
#> [2] <body class="mediawiki ltr sitedir-ltr mw-hide-empty-elt ns-0 ns-subject ...
We use tools from rvest to identify particular parts. In our case, we want to use html_nodes and tell it to get the .wikitable that we saw earlier.
jwebb_data %>%
html_nodes(".wikitable")
#> {xml_nodeset (3)}
#> [1] <table class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; float:center; margin:1 ...
#> [2] <table class="wikitable" style="font-size:88%; float:right; margin-left:0 ...
#> [3] <table class="wikitable" style="font-size:0.9em; float:right; margin-left ...
We see here that we have three tables, let’s extract the tables from each of these, using map to run html_table on each, using fill = TRUE to fill rows with fewer than max columns with NAs, to ensure we get proper data back.
jwebb_data %>%
html_nodes(".wikitable") %>%
map(html_table, fill = TRUE)
#> [[1]]
#> X1
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 Name
#> 3 IRT
#> 4 Infrared Space Observatory (ISO)[57]
#> 5 Hubble Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS)
#> 6 Hubble Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS)
#> 7 Spitzer Space Telescope
#> 8 Hubble Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3)
#> 9 Herschel Space Observatory
#> 10 JWST
#> X2
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 Year
#> 3 1985
#> 4 1995
#> 5 1997
#> 6 1997
#> 7 2003
#> 8 2009
#> 9 2009
#> 10 2021
#> X3
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 Wavelength
#> 3 1.7–118 μm
#> 4 2.5–240 μm
#> 5 0.115–1.03 μm
#> 6 0.8–2.4 μm
#> 7 3–180 μm
#> 8 0.2–1.7 μm
#> 9 55–672 μm
#> 10 0.6–28.5 μm
#> X4
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 Aperture
#> 3 0.15 m
#> 4 0.60 m
#> 5 2.4 m
#> 6 2.4 m
#> 7 0.85 m
#> 8 2.4 m
#> 9 3.5 m
#> 10 6.5 m
#> X5
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 Cooling
#> 3 Helium
#> 4 Helium
#> 5 Passive
#> 6 Nitrogen, later cryocooler
#> 7 Helium
#> 8 Passive + Thermo-electric [58]
#> 9 Helium
#> 10 Passive + cryocooler (MIRI)
#> X6
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 <NA>
#> 3 <NA>
#> 4 <NA>
#> 5 <NA>
#> 6 <NA>
#> 7 <NA>
#> 8 <NA>
#> 9 <NA>
#> 10 <NA>
#> X7
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 <NA>
#> 3 <NA>
#> 4 <NA>
#> 5 <NA>
#> 6 <NA>
#> 7 <NA>
#> 8 <NA>
#> 9 <NA>
#> 10 <NA>
#> X8
#> 1 Selected space telescopes and instruments[56]
#> 2 <NA>
#> 3 <NA>
#> 4 <NA>
#> 5 <NA>
#> 6 <NA>
#> 7 <NA>
#> 8 <NA>
#> 9 <NA>
#> 10 <NA>
#>
#> [[2]]
#> Year Events
#> 1 1996 NGST started.
#> 2 2002 named JWST, 8 to 6 m
#> 3 2004 NEXUS cancelled [60]
#> 4 2007 ESA/NASA MOU
#> 5 2010 MCDR passed
#> 6 2011 Proposed cancel
#> 7 2021 Planned launch
#>
#> [[3]]
#> Year Plannedlaunch
#> 1 1997 2007 [80]
#> 2 1998 2007 [85]
#> 3 1999 2007 to 2008 [86]
#> 4 2000 2009 [44]
#> 5 2002 2010 [87]
#> 6 2003 2011 [88]
#> 7 2005 2013
#> 8 2006 2014
#> 9 2008, Preliminary Design Review 2008, Preliminary Design Review
#> 10 2008 2014
#> 11 2010, Critical Design Review 2010, Critical Design Review
#> 12 2010 2015 to 2016
#> 13 2011 2018
#> 14 2013 2018
#> 15 2017 2019 [94]
#> 16 2018 2020 [95]
#> 17 2018 2021 [96]
#> 18 2020 2021 [3]
#> Budget Plan(Billion USD)
#> 1 0.5 [80]
#> 2 1 [59]
#> 3 1 [59]
#> 4 1.8 [59]
#> 5 2.5 [59]
#> 6 2.5 [59]
#> 7 3 [89]
#> 8 4.5 [90]
#> 9 2008, Preliminary Design Review
#> 10 5.1 [91]
#> 11 2010, Critical Design Review
#> 12 6.5[citation needed]
#> 13 8.7 [92]
#> 14 8.8 [93]
#> 15 8.8
#> 16 ≥8.8
#> 17 9.66
#> 18 ≥10 [34]
We want the third table, so we use pluck, and convert it to a tibble for nice printing
jwebb_data %>%
html_nodes(".wikitable") %>%
map(html_table, fill = TRUE) %>%
pluck(3) %>%
as_tibble()
#> # A tibble: 18 x 3
#> Year Plannedlaunch `Budget Plan(Billion USD)`
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1997 2007 [80] 0.5 [80]
#> 2 1998 2007 [85] 1 [59]
#> 3 1999 2007 to 2008 [86] 1 [59]
#> 4 2000 2009 [44] 1.8 [59]
#> 5 2002 2010 [87] 2.5 [59]
#> 6 2003 2011 [88] 2.5 [59]
#> 7 2005 2013 3 [89]
#> 8 2006 2014 4.5 [90]
#> 9 2008, Preliminary Desig… 2008, Preliminary Design… 2008, Preliminary Design …
#> 10 2008 2014 5.1 [91]
#> 11 2010, Critical Design R… 2010, Critical Design Re… 2010, Critical Design Rev…
#> 12 2010 2015 to 2016 6.5[citation needed]
#> 13 2011 2018 8.7 [92]
#> 14 2013 2018 8.8 [93]
#> 15 2017 2019 [94] 8.8
#> 16 2018 2020 [95] ≥8.8
#> 17 2018 2021 [96] 9.66
#> 18 2020 2021 [3] ≥10 [34]
We get rid of rows 9 and 11 as they are rows that span the full table and aren’t proper data in this context, and then run clean_names from janitor to make the variable names nicer.
jwebb_data %>%
html_nodes(".wikitable") %>%
map(html_table, fill = TRUE) %>%
pluck(3) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
slice(-9,
-11) %>%
clean_names()
#> # A tibble: 16 x 3
#> year plannedlaunch budget_plan_billion_usd
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1997 2007 [80] 0.5 [80]
#> 2 1998 2007 [85] 1 [59]
#> 3 1999 2007 to 2008 [86] 1 [59]
#> 4 2000 2009 [44] 1.8 [59]
#> 5 2002 2010 [87] 2.5 [59]
#> 6 2003 2011 [88] 2.5 [59]
#> 7 2005 2013 3 [89]
#> 8 2006 2014 4.5 [90]
#> 9 2008 2014 5.1 [91]
#> 10 2010 2015 to 2016 6.5[citation needed]
#> 11 2011 2018 8.7 [92]
#> 12 2013 2018 8.8 [93]
#> 13 2017 2019 [94] 8.8
#> 14 2018 2020 [95] ≥8.8
#> 15 2018 2021 [96] 9.66
#> 16 2020 2021 [3] ≥10 [34]
Finally we parse_number over all columns, using across and friends:
jwebb <- jwebb_data %>%
html_nodes(".wikitable") %>%
map(html_table, fill = TRUE) %>%
pluck(3) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
slice(-9,
-11) %>%
clean_names() %>%
mutate(across(everything(), parse_number))
jwebb
#> # A tibble: 16 x 3
#> year plannedlaunch budget_plan_billion_usd
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1997 2007 0.5
#> 2 1998 2007 1
#> 3 1999 2007 1
#> 4 2000 2009 1.8
#> 5 2002 2010 2.5
#> 6 2003 2011 2.5
#> 7 2005 2013 3
#> 8 2006 2014 4.5
#> 9 2008 2014 5.1
#> 10 2010 2015 6.5
#> 11 2011 2018 8.7
#> 12 2013 2018 8.8
#> 13 2017 2019 8.8
#> 14 2018 2020 8.8
#> 15 2018 2021 9.66
#> 16 2020 2021 10
We now want to check we can make a similar plot to XKCD, let’s plot the data, with a linear model fit overlayed:
gg_jwebb <- ggplot(jwebb,
aes(x = year,
y = plannedlaunch)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm",
se = FALSE)
gg_jwebb
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula 'y ~ x'
OK but now we need to extend out the plot to get a sense of where it can extrapolate to. Let’s extend the limits, and add an abline, a line with slope of 1 and intercept through 0.
gg_jwebb +
lims(x = c(1997,2030),
y = c(1997,2030)) +
geom_abline(linetype = 2)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula 'y ~ x'
We want to extend that fitted line ahead, so let’s fit a linear model to the data with plannedlaunch being predicted by year (which is what geom_smooth(method = "lm") does under the hood):
lm_jwebb <- lm(plannedlaunch ~ year, jwebb)
Then we use augment to predict some new data for 1997 through to 2030:
library(broom)
new_data <- tibble(year = 1997:2030)
jwebb_predict <- augment(lm_jwebb, newdata = new_data)
jwebb_predict
#> # A tibble: 34 x 2
#> year .fitted
#> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 1997 2007.
#> 2 1998 2008.
#> 3 1999 2008.
#> 4 2000 2009.
#> 5 2001 2010.
#> 6 2002 2010.
#> 7 2003 2011.
#> 8 2004 2012.
#> 9 2005 2012.
#> 10 2006 2013.
#> # … with 24 more rows
Now we can add that to our plot:
gg_jwebb_pred <- gg_jwebb +
lims(x = c(1997,2030),
y = c(1997,2030)) +
geom_abline(linetype = 2) +
geom_line(data = jwebb_predict,
colour = "steelblue",
linetype = 3,
size = 1,
aes(x = year,
y = .fitted))
gg_jwebb_pred
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula 'y ~ x'
And finally add some extra details that XKCD had, using geom_vline and geom_label_rep
library(ggrepel)
gg_jwebb_pred +
geom_vline(xintercept = 2026.5,
linetype = 2,
colour = "orange") +
labs(title = "Predicted James Webb Launch",
subtitle = "Did Randell Munroe get it right?") +
geom_label_repel(data = data.frame(year = 2026.5,
plannedlaunch = 2026.5),
label = "2026",
nudge_x = -2,
nudge_y = 3,
segment.colour = "gray50")
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula 'y ~ x'
Did he get it right?
Yes, of course. Why did I ever doubt him.